Nutrition myths are everywhere. You hear them at dinner tables, read them in magazines, and see them splashed across social media. These myths, no matter how well-intentioned, can be misleading. They’ve been passed down through generations, reinforced by trends, and even bolstered by some health professionals. But in today’s world, with endless access to scientific studies and expert voices, there’s no reason to keep clinging to these outdated beliefs.
We live in an age of information—and misinformation. The stakes are high when it comes to nutrition myths. Believing in the wrong information can lead to unhealthy habits, wasted time, and unnecessary restrictions. Worse yet, some myths can even harm your health, leaving you nutrient-deficient or overly reliant on supplements and fad diets.
It’s time to debunk these 11 nutrition myths and look at what science actually says. Prepare to unlearn a few things you’ve probably heard countless times. And by the end, you’ll have a clearer view of what truly fuels a healthy body.
1. Myth: Carbs Are the Enemy

Carbs have become a four-letter word in modern diets. Many believe that cutting out carbs is the secret to shedding pounds. But not all carbs are created equal. Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are packed with essential nutrients that support everything from energy levels to heart health. In fact, carbs are the body’s primary energy source, especially for the brain.
Low-carb diets might deliver quick results, but long-term restriction can leave you drained and irritable. Instead of eliminating carbs, focus on choosing complex ones—like quinoa, oats, and brown rice. These provide lasting energy without the blood sugar spikes associated with refined carbs.
2. Myth: You Need to Eat Small Meals Frequently to Boost Metabolism

Some people swear by the “six small meals a day” rule to keep their metabolism revved. But studies have shown that meal frequency doesn’t significantly impact your metabolic rate. The real factors that influence metabolism are muscle mass, age, and activity level.
Eating several small meals might prevent overeating if it keeps your appetite in check. But for others, it can lead to constant snacking, which isn’t necessarily beneficial. What matters most is finding a routine that works for your lifestyle and hunger levels, whether that’s three meals or six.
3. Myth: All Fats Are Bad for You
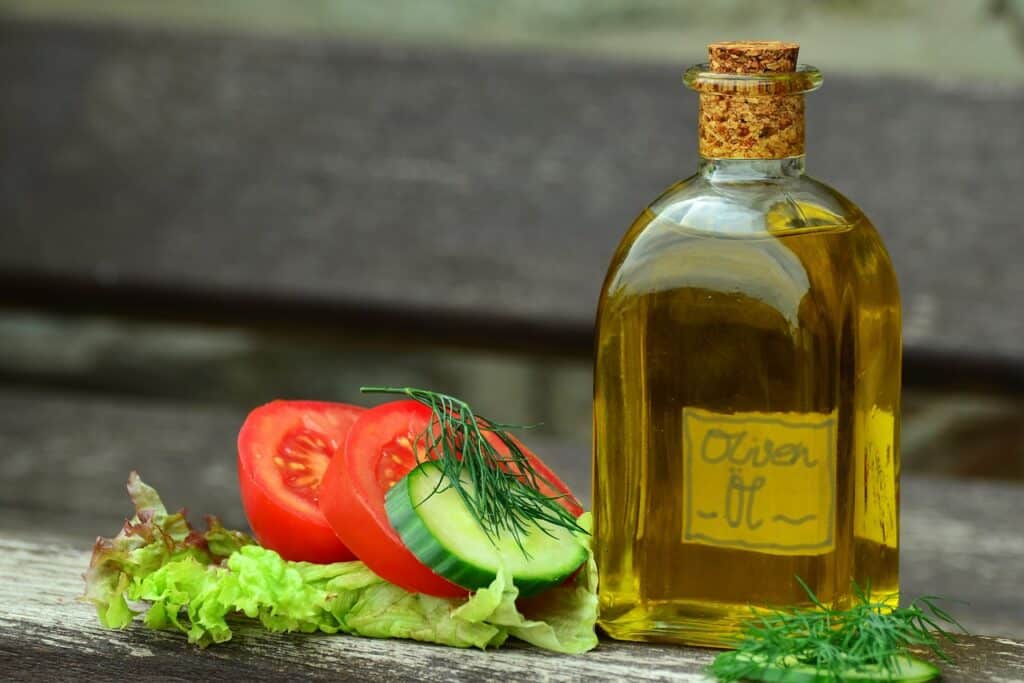

The fear of fat has led countless people to reach for low-fat everything, believing it’s the healthier option. But not all fats are harmful. Healthy fats—found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil—play a vital role in brain function, hormone production, and nutrient absorption.
Avoiding all fats can actually lead to deficiencies, as some vitamins require fat to be absorbed properly. So next time you see a fat-free label, remember: some fats are necessary for a balanced diet. The key is choosing unsaturated fats and limiting saturated and trans fats.
4. Myth: Detox Diets and Juices Cleanse Your Body

Detox diets and juice cleanses have surged in popularity, promising to “reset” or “cleanse” the body of toxins. The truth? Your liver and kidneys are already working around the clock to filter out toxins. No juice can do it better.
While detox drinks may seem healthy, they often lack the fiber and protein necessary for balanced nutrition. Instead of spending on expensive cleanses, focus on whole foods, hydration, and exercise—your body’s natural detox methods.
5. Myth: High-Protein Diets Are Best for Everyone

Protein has become a dietary buzzword, with high-protein diets praised for building muscle and shedding fat. But more isn’t always better. Excess protein can strain the kidneys and lead to dehydration if you’re not careful.
The average person needs around 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily, which is achievable through a balanced diet. Unless you’re an elite athlete, there’s no need to obsess over protein shakes and bars. Stick with whole foods—lean meats, beans, nuts, and dairy—to meet your needs naturally.
6. Myth: Eating Late at Night Leads to Weight Gain

Many believe that a late-night snack is a surefire way to pack on pounds. But weight gain isn’t dictated by the clock; it’s a matter of calories in versus calories out. Eating a balanced snack in the evening won’t make you gain weight as long as you’re staying within your daily calorie range.
If late-night eating is a pattern, it might be worth examining why you’re snacking. Are you hungry, or just eating out of boredom? Reframe your habits instead of stressing over the clock. Healthy nighttime snacks—like yogurt, a handful of nuts, or fruit—won’t derail your diet.
7. Myth: Natural Sugars Are Always Healthier Than Refined Sugars

There’s a common misconception that natural sugars, like honey and maple syrup, are “better” for you than refined sugars. While these options may have trace amounts of vitamins and minerals, they still impact blood sugar levels in much the same way as regular sugar.
Excessive sugar—whether natural or refined—can lead to health issues over time, including obesity and diabetes. Moderation is key. Enjoy natural sweeteners, but remember, they’re still sugar. Stick to small amounts to avoid unnecessary calorie spikes.
8. Myth: Breakfast Is the Most Important Meal of the Day

Breakfast has long been touted as the day’s most important meal, believed to jumpstart metabolism and improve focus. But recent studies show that breakfast isn’t essential for everyone. Some people thrive on intermittent fasting, skipping breakfast altogether.
Whether or not breakfast works for you depends on your personal hunger cues and schedule. If you’re genuinely hungry in the morning, have a balanced meal with protein, carbs, and healthy fats. If you’re not, it’s okay to wait. Listen to your body, not outdated advice.
9. Myth: You Can’t Get Enough Protein from a Plant-Based Diet

A plant-based diet doesn’t mean you’ll be protein-deficient. Beans, lentils, tofu, quinoa, and even vegetables contain protein. It’s true that plant-based proteins are less concentrated than animal sources, but with the right balance, they can meet all of your dietary needs.
Plant-based diets have been linked to lower risks of heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. And protein isn’t the only factor to consider in a healthy diet. So if you’re going plant-based, focus on variety and include whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
10. Myth: Drinking Lots of Water Can Flush Out Fat

We’ve all heard that guzzling water is essential for weight loss, with some believing it can even flush out fat. While staying hydrated is crucial, water alone won’t melt away fat. Fat loss happens when you burn more calories than you consume, through a combination of diet and exercise.
Water does have an indirect role—it helps control appetite and supports metabolism. But no amount of water alone will make you lose fat. So drink up, but don’t rely on water alone to do the heavy lifting.
11. Myth: Multivitamins Can Replace a Balanced Diet

Multivitamins seem like an easy fix, providing a broad spectrum of nutrients in a single pill. But no supplement can replicate the complex blend of vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants found in whole foods. While multivitamins can be helpful for certain deficiencies, they’re not a substitute for a healthy diet.
Whole foods are packed with compounds that interact in ways supplements can’t mimic. So rather than popping pills, focus on eating a colorful variety of fruits, vegetables, grains, and lean proteins.
Conclusion
In the end, the most shocking part about nutrition myths is how pervasive they’ve become. With so much information floating around, it’s easy to fall into the trap of believing outdated or oversimplified advice. But understanding the science behind nutrition is more important now than ever. Your health depends on it.
Breaking free from these nutrition myths isn’t just about eating better; it’s about making informed choices that suit your body’s needs. Nutrition is personal, and no one-size-fits-all rule can cover everyone’s unique requirements. By ditching these myths, you’re freeing yourself from needless restrictions and embracing a more flexible, balanced approach to health.
So, the next time you hear someone proclaim the dangers of carbs or the virtues of detoxing, remember that sound nutrition is grounded in balance, variety, and listening to your body—not in following the latest trends. Use this knowledge to fuel your health journey with clarity and confidence.
What did you thing of our 11 list of nutrition myths? Let us know in the comment section below.
Check out 11 Breathtaking National Parks.